磁盘性能测试
|Word Count:2.2k|Reading Time:10mins|Post Views:
前些天正好有个外协部门需要利旧,需要根据阿里云的测试流程对新华三的服务器和NVME磁盘进行一下测试,所以把手头的资料整理一下。

2023.05 摄于洛阳·龙门石窟
存储
一开始想写点什么来着,后来发现少数派上的文章写的非常棒,就一并转贴了
- 存储设备的诞生与历史
- 机械硬盘的原理与参数详解
- 固态硬盘的历史、结构与原理
- 固态硬盘的参数解读与实际性能
- 运行内存都在运行什么?
- 理解U盘、内存卡、移动硬盘和手机存储芯片构造
文牍
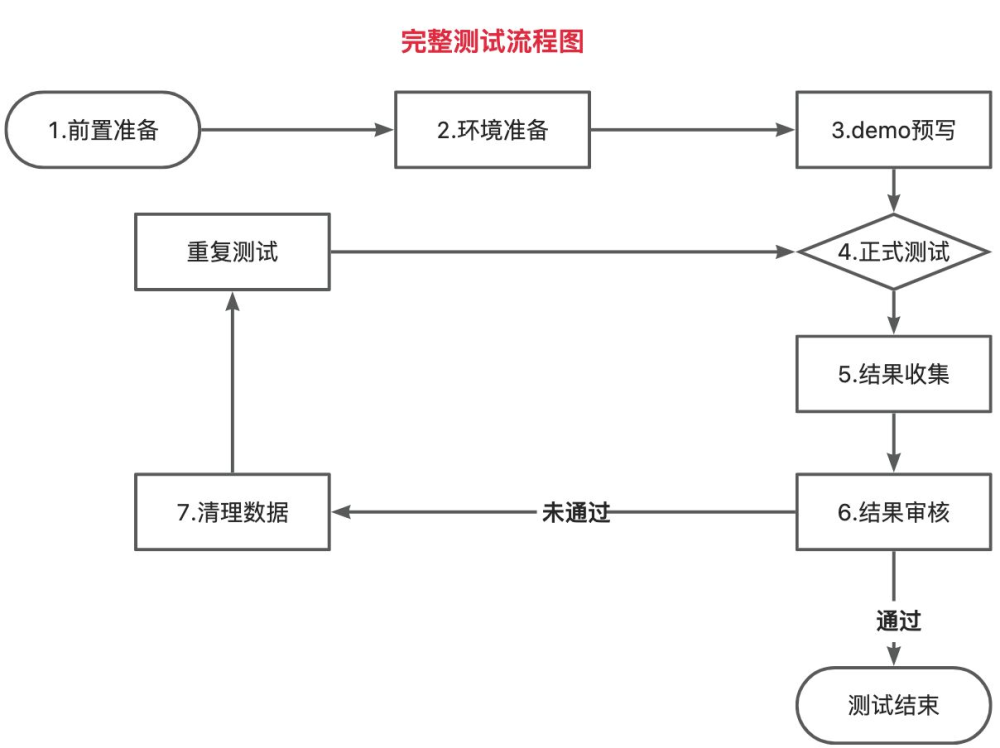
测试流程

测试用例

测试报告

测试
FIO
简介
FIO是一个用于测试磁盘IOPS性能的工具,可以对本地存储或者远程共享进行压力测试和验证,并能够给出磁盘性能的指标。FIO能够按照随机读、随机写、读写混合等不同IO模式对压测对象进行性能测试。
使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| # 检查是否4k对齐
[root@zhangjiakou ~]# fdisk -lu
Disk /dev/vda: 40 GiB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: D7B18C8A-605C-42E0-94BF-A4A0B2DE0204
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/vda1 2048 4095 2048 1M BIOS boot
/dev/vda2 4096 208895 204800 100M EFI System
/dev/vda3 208896 83886046 83677151 39.9G Linux filesystem
# 安装
[root@zhangjiakou ~]# dnf install -y libaio libaio-devel fio
# 测试云盘的随机写IOPS:
fio -direct=1 -iodepth=128 -rw=randwrite -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=Rand_Write_Testing
# 测试云盘的随机读IOPS:
fio -direct=1 -iodepth=128 -rw=randread -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=Rand_Read_Testing
#测试云盘的顺序写吞吐量:
fio -direct=1 -iodepth=64 -rw=write -ioengine=libaio -bs=1024k -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=Write_PPS_Testing
#测试云盘的顺序读吞吐量:
fio -direct=1 -iodepth=64 -rw=read -ioengine=libaio -bs=1024k -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=Read_PPS_Testing
#测试云盘的随机写时延:
fio -direct=1 -iodepth=1 -rw=randwrite -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -size=1G -numjobs=1 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=Rand_Write_Latency_Testing
#测试云盘的随机读时延:
fio -direct=1 -iodepth=1 -rw=randread -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -size=1G -numjobs=1 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=Rand_Read_Latency_Testing
|
参数
| 参数 |
说明 |
| direct |
表示是否使用direct I/O。默认值:1。值为1:表示使用direct I/O,忽略I/O缓存,数据直写。值为0:表示不使用direct I/O。 |
| iodepth |
表示测试时的IO队列深度。例如-iodepth=128表示FIO控制请求中的I/O最大个数为128。 |
| rw |
表示测试时的读写策略。您可以设置为:randwrite:随机写。randread:随机读。read:顺序读。write:顺序写。randrw:混合随机读写。 |
| ioengine |
表示测试时FIO选择哪种I/O引擎,通常选择libaio,更符合日常应用模式,更多的选择请查阅FIO官方文档。 |
| bs |
表示I/O单元的块大小(block size)。默认值:4 KiB。读取和写入的值可以以read、write格式单独指定,其中任何一个都可以为空以将该值保留为其默认值。 |
| size |
表示测试文件大小。FIO会将指定的文件大小全部读/写完成,然后才停止测试,除非受到其他选项(例如运行时)的限制。如果未指定该参数,FIO将使用给定文件或设备的完整大小。也可以将大小作为1到100之间的百分比给出。例如指定size=20%,FIO将使用给定文件或设备完整大小的20%空间。 |
| numjobs |
表示测试的并发线程数。默认值:1。 |
| runtime |
表示测试时间,即FIO运行时长。如果未指定该参数,则FIO会持续将上述size指定大小的文件,以每次bs值为块大小读/写完。 |
| group_reporting |
表示测试结果显示模式。如果指定该参数,测试结果会汇总每个进程的统计信息,而不是以不同任务来统计信息。 |
| filename |
表示待测试的对象路径,路径可以是云盘设备名称或者一个文件地址。本文中的FIO测试全部是以整盘为测试对象,不含文件系统,即裸盘测试。同时为了避免误测试到其他盘导致数据被破坏,本示例地址为/dev/your_device,请您正确替换。 |
| name |
表示测试任务名称,可以随意设定。例如本示例的Rand_Write_Testing。 |
实例
以下是某次执行测试的实际脚本,需要提前预制安装fio、libaio、nvme、storcli这几个工具。storcli需要到博通网站上下载RPM包。
执行脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| #!/bin/bash
dir=`pwd`
yum install -y fio libaio libaio-devel nvmecli
#rpm -ivh libaio-devel-0.3.109-13.1.alios7.x86_64.rpm
#tar -zxvf fio-fio-2.16.tar.gz
#cd fio-fio-2.16
#./configure
#make
#make install
#cd $dir
controller=`lspci -n|grep -E "1000|9005"`
if [[ ${controller} =~ 1000 ]];
then
# rpm -ivh storcli-007.0504.0000.0000-1.x86_64.rpm
storcli64 show all >> lsi_controller_info.txt
elif [[ ${controller} =~ 9005 ]];
then
./arcconf getconfig 1 ad|grep -iE "controllers found|controller model"|sort -u >> pmc_controller_info.txt
fi
for dev in `ls /sys/block/ |grep -E sd[b-z] & ls /sys/block/ |grep -E "ram*|sd[a-z][a-z]|nvme*"`
do
rootdev=`lsblk |grep ${dev}1|grep /boot`
if [ -z "$rootdev" ];
then
cd $dir
mkdir fiotest-${dev} >/dev/null 2>&1
cd $dir/fiotest-${dev}
if [[ ${dev} =~ nvme ]]
then
nvme format -s 1 /dev/$dev
sleep 5
cp -f ../test-fio-nvme.sh ./ >/dev/null 2>&1
cp -f ../get_result.sh ./ >/dev/null 2>&1
sh test-fio-nvme.sh -p444 $dev &
sleep 5
else
cp -f ../test-fio.sh ./ >/dev/null 2>&1
cp -f ../get_result.sh ./ >/dev/null 2>&1
sh test-fio.sh -p555 $dev &
sleep 5
fi
else
echo "skip $dev ,this is sysdisk..."
fi
done
|
结果脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| #/bin/sh
function get_rw_result()
{
if [ $# -lt 1 ]
then
echo "please input filename:"
exit
else
rw=`cat $1 | grep -i bs | grep -i rw | awk '{print $3}' | awk -F ',' '{print $1}'`
bs=`cat $1 | grep -i bs | grep -i rw | awk '{print $4}' | awk -F '/' '{print $1}'`
depth=`cat $1 | grep -i bs | grep -i rw | awk '{print $6}' | awk -F '=' '{print $2}'`
job=`cat $1 |grep -i starting|awk '{print $2}'`
bw=`cat $1 | grep -i iops | awk -F ',' '{print $2}'`
iops=`cat $1 | grep -i iops | awk -F ',' '{print $3}'`
lat=`cat $1 | grep -i -w lat | grep -i avg | awk -F ',' '{print $3}' | awk '$1=$1'`
unit=`cat $1 | grep -i -w lat | grep -i avg | awk '{print $2}' | cut -b 2-5 | awk '{printf("%s ",$0)}'`
echo ${bs:3},${rw:3},${depth},${job},${bw:4},${iops:6},${lat:4},${unit} >> re.csv
fi
}
function get_mix_result()
{
if [ $# -lt 1 ]
then
echo "please input filename:"
exit
else
#mix_rw=`cat $1 | grep -i bs | grep -i rw | awk '{print $3}' | awk -F ',' '{print $1}'`
mix_rw=`echo $1 | awk -F '_' '{print $1}'`
mix_bs=`cat $1 | grep -i bs | grep -i rw | awk '{print $4}' | awk -F '/' '{print $1}'`
mix_read_bw=`cat $1 | grep -i iops | grep -i read | awk -F ',' '{print $2}' | awk '$1=$1'`
mix_write_bw=`cat $1 | grep -i iops | grep -i write | awk -F ',' '{print $2}' | awk '$1=$1'`
mix_read_iops=`cat $1 | grep -i iops | grep -i read | awk -F ',' '{print $3}' | awk '$1=$1'`
mix_write_iops=`cat $1 | grep -i iops | grep -i write | awk -F ',' '{print $3}' | awk '$1=$1'`
mix_read_lat=`cat $1 | grep -i -w lat | grep -i avg | awk 'NR==1{print}' | awk -F ',' '{print $3}' | awk '$1=$1'`
mix_write_lat=`cat $1 | grep -i -w lat | grep -i avg | awk 'NR==2{print}' | awk -F ',' '{print $3}' | awk '$1=$1'`
mix_unit=`cat $1 | grep -i -w lat | grep -i avg | awk '{print $2}' | cut -b 2-5 | awk '{printf("%s ",$0)}'`
echo ${mix_bs:3},${mix_rw},${mix_read_bw:3},${mix_write_bw:3},${mix_read_iops:5},${mix_write_iops:5},${mix_read_lat:4},${mix_write_lat:4},${mix_unit} >> mix.csv
fi
}
get_rw_result $1
|
压测脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| #/bin/sh
#Author WB-txq457949
#Date 2019/10/04
#Set Runtime & Drive
Test_Device=$2
while true
do
#FIO Test
nvme smart-log /dev/${Test_Device} >>before-smart.log
fio --filename=/dev/${Test_Device} --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --thread=1 --numjobs=1 --iodepth=16 --rw=randread --bs=16k --runtime=12h --log_avg_msec=1000 --write_lat_log=16k_1job_16iodepth_randread --write_iops_log=iops_16k_1job_16iodepth_randread --size=100% --group_reporting --name=mytest >randread.rec
fio --filename=/dev/${Test_Device} --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --thread=1 --numjobs=1 --iodepth=16 --rw=randwrite --bs=16k --runtime=12h --log_avg_msec=1000 --write_lat_log=16k_1job_16iodepth_randwrite --write_iops_log=iops_16k_1job_16iodepth_randwrite --size=100% --group_reporting --name=mytest > randwrite.rec
fio --filename=/dev/${Test_Device} --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --thread=1 --numjobs=1 --iodepth=16 --rw=randrw --rwmixwrite=30 --bs=16k --runtime=6d --log_avg_msec=1000 --write_lat_log=16k_1job_16iodepth_mixreadwrite --write_iops_log=iops_16k_1job_16iodepth_mixreadwrite --size=100% --group_reporting --name=mytest > mixreadwrite.rec
nvme smart-log /dev/${Test_Device} >>affter-smart.log
echo "BS,Modes,Iodepth,numjobs,BW,IOPS,Latency,Unit" > re.csv
#echo "Mix_BS,Mix_Mode,Read_BW,Write_BW,Read_IOPS,Write_IOPS,Read_Latency,Write_Latency,Lat_Unit" > mix.csv
for result in `ls *.rec`
do
sh get_result.sh $result
done
done
|